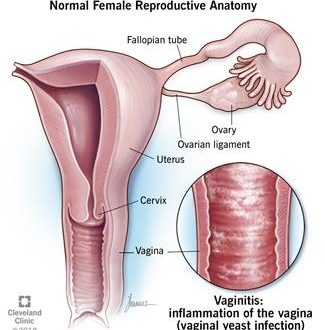
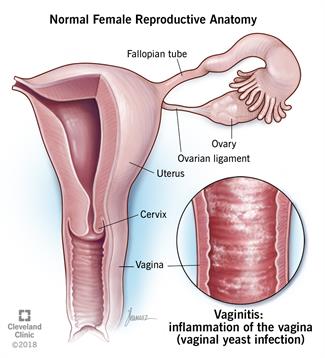
Vaginitis is an inflammation or infection of the vaginal canal. The vulva, which is the external part of a woman’s genitals, can also be affected where this is then known as vulvovaginitis. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as bacteria or fungal infections while others can be substances found in topical lotions, beauty products or even clothes coming in contact with this area. Several other conditions can lead to vaginitis, such as atrophic vaginitis, which is caused by lack of estrogen.
Symptoms of vaginitis can range from asymptomatic (showing no symptoms) to painful. The condition can be infectious or non-infectious. Women who are pregnant can develop an inflammatory case of vaginitis secondary to hormonal changes, and it can also occur with oral antibiotic use. Antibiotic treatment for another infection elsewhere in the body can affect the normal vaginal bacteria and allow for the overgrowth of yeast, leading to a yeast infection and inflammation.Burning sensations, redness, vaginal discharge, and sometimes painful urination are all signs and symptoms of vaginitis. It is also worth noting that the disease can sometimes coexist with a urinary tract infection. In this situation, antibiotics will be required to treat the urine infection.
Vaginitis is particularly common in women who are in their reproductive years. It can be caused by low estrogen levels and underdeveloped labia minora. Vulvovaginitis is common among teenagers.
TYPES OF VAGINITIS
There are several types of vaginitis depending upon the cause. The most common are:
- Candida or Yeast infections
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Trichomoniasis Vaginitis
- Chlamydia
- Viral Vaginitis
- Non-Infectious Vaginitis
- Atrophic Vaginitis
CAUSES OF VAGINITIS
Vaginitis is a broad term that refers to a variety of infections and inflammatory disorders that affect the vaginal area. Determining the exact origin of infection is essential for accurate diagnosis. The following are some of the most common causes of vaginitis.
CANDIDA ALBICAN OR YEAST INFECTION
Candida albicans is a yeast-caused fungal infection. This infection can be caused by more than 20 different yeast species. Candida albicans is the most prevalent of them. This yeast is one of the vagina flora’s microorganisms (a group of micro-organisms that lives in the vagina). Candida albicans coexists quietly in the vagina with other bacteria and yeast. However, certain factors cause them to thrive and multiply. They begin to dominate the vagina as their numbers multiply and disrupt the body’s general equilibrium. When this yeast grows too much, it might cause infections such as vaginitis. Yeast infections do not usually produce a foul odor, but the vaginal area may become red and itchy, and you may feel a burning sensation when peeing. Yeast infections are not always caused by sexual contact, though having several sexual partners raise your risk.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS (BV)
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a condition in which the bacteria in the vagina are imbalance. This may result in inflammation, itching and unpleasant vaginal discharge with a foul odor. It is a mild infection that is usually harmless and treatable with medication. BV is most common in women who have multiple sex partners but it can also affect non-sexually active women. It is unclear what causes the imbalance. Bacterial vaginosis can exist without causing symptoms.
TRICHOMONAS VAGINITIS
Trichomonas vaginitis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by trichomonas vaginalis, a small protozoan parasite. Within a month of infection, symptoms usually appear. However, in certain circumstances, people do not show any signs or symptoms at all and because the symptoms are identical to those of many other STDs (sexually transmitted diseases), early identification is challenging. The infection is characterized by soreness, pain, swelling and foul discharge. The infection is seen in the vaginal and urethral areas of women. Sexual partners should be treated and abstain from sex for at least seven days after treatment since it is sexually transmitted.
CHLAMYDIA
The most common sexually transmitted infection is chlamydia (STI). Chlamydial vaginitis is most common in young adults between the ages of 15 and 24, especially those who have several sexual partners. While antibiotics can be used to treat chlamydia infections, the best treatment for chlamydia is prevention. Condoms and dental dams should be used correctly and consistently to reduce your chance of developing chlamydia and other sexually transmitted illnesses. To avoid re-infection, sex partners should be monitored and treated appropriately.
VIRAL VAGINITIS
This is another prevalent cause of vaginitis. The Herpes simplex virus is a common cause of viral vaginitis. It is spread by sexual contact and is frequently accompanied by pain from sores or lesions that develop on the vulva or vagina. During oral sex, the virus could potentially be spread to the mouth. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) may also cause vaginitis, which can lead to genital warts on the vulva, vagina, rectum, and groin. Most HPV warts may be detected with a physical examination, however you may discover white, grey, pink, or purple warts on your genitalia.
Culled from Thisdaylive.com
 Quelins – Relationship, Sex, Marriage and Health News around the world Quelins Blog is an online magazine about relationships, love, information about marriage, partnerships and issues patterning to all that.
Quelins – Relationship, Sex, Marriage and Health News around the world Quelins Blog is an online magazine about relationships, love, information about marriage, partnerships and issues patterning to all that.